Blood glucose in diabetes
What is blood sugar (glucose)?
From a chemical perspective, glucose is categorized as a simple sugar, meaning it is not bonded with other sugar molecules. Thus, glucose can directly enter the bloodstream without needing to be broken down by digestive enzymes.
Glucose serves as a crucial energy source for body cells, particularly nerve cells. Its transport to cells requires the hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. Nerve cells and red blood cells are exceptions, as they absorb glucose without the need for insulin.
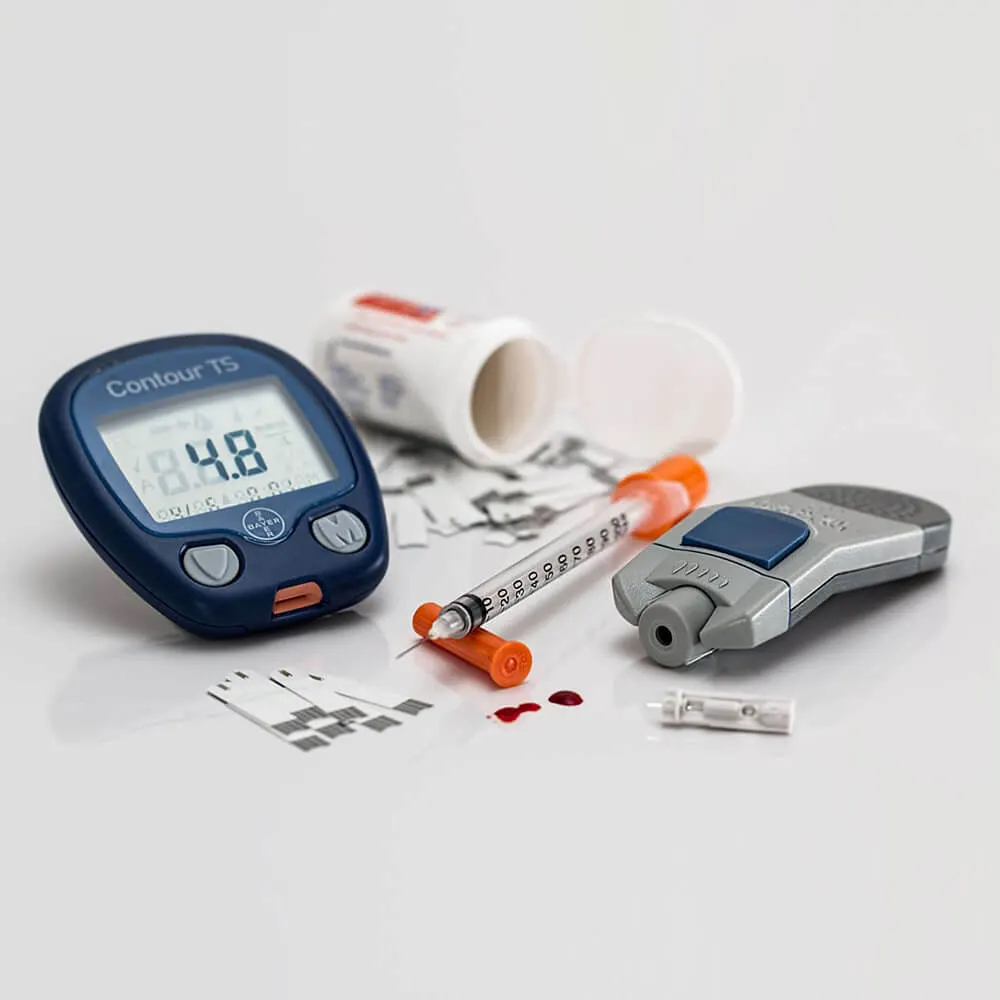
Diabetes, a blood glucose meter, insulin syringes, and tablets
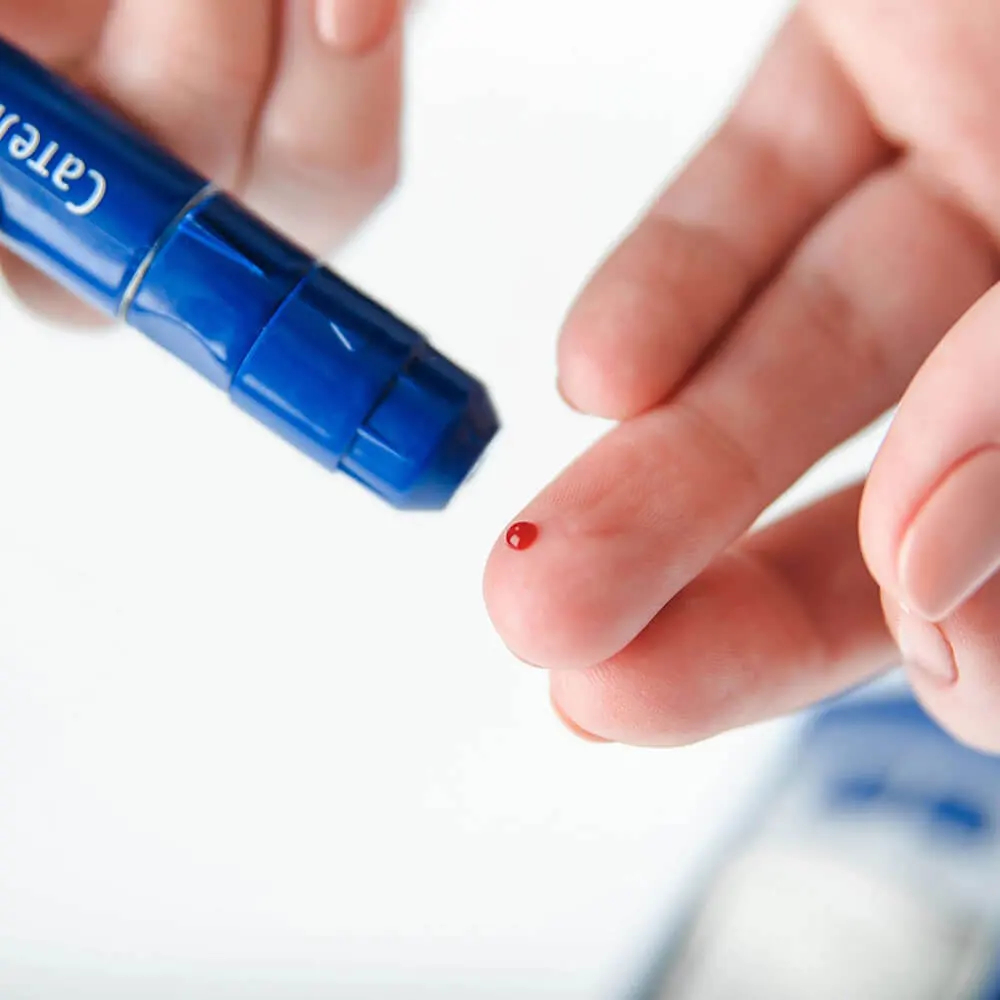
For blood glucose measurement, use a fine lancet to obtain a drop of blood from the fingertip.
When should the blood glucose level be taken?
It is important to measure the glucose level if there is a strong suspicion of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes can develop rapidly, within days or weeks, and presents symptoms such as frequent urination, intense thirst, fatigue, weight loss, and general lethargy.

What are the normal blood glucose levels?
In people without diabetes, fasting blood glucose levels are below 100 milligrams per decilitre, or less than 5.6 millimoles per litre. Typically, after eating, blood glucose levels increase somewhat but do not exceed 140 milligrams per decilitre.
Diabetes mellitus is diagnosed only if blood glucose levels are higher than 126 milligrams per decilitre in a fasting state or surpass 200 milligrams following a meal.
Fasting values ranging from 100 to 125 mg/dl might already suggest an early stage of type 2 diabetes. A glucose tolerance test (OGTT) can be used to confirm the diagnosis.