FAQs on Stevia | Stevia FAQ
Frequently asked questions about Stevia: our FAQ section covers the most common inquiries and provides answers. Gain comprehensive insights about Stevia.
To assist in your purchasing choice, we address various questions related to its advantages and applications.
How do you substitute sugar with Stevia?
Why might Stevia taste bitter?
Why are Stevia prices so varied?
We also offer tips for different Stevia products.
If you still have queries, feel free to reach out to us.
We are here to assist you.
Frequently asked questions about Stevia
Stevia is a natural sweetener that comes from the leaves of the Stevia plant.
It is extremely sweet and contains zero calories, making it a favored choice for those looking to cut down on sugar.
Stevia is commonly used in tablet form and can be found in many processed foods and drinks as an ingredient or natural sweetener.
Because of its high sweetness compared to regular sugar, only a small quantity of Stevia is required to achieve similar sweetness levels.
Indigenous communities in South America have used Stevia as a sweetener for hundreds of years. Scientific studies on Stevia started in the 1930s. Japan initiated commercial use of Stevia in the 1970s. Over recent decades, Stevia has also become popular globally. Today, Stevia is accessible as a sweetener in numerous countries.
Yes, diabetics can use Steviol glycosides. These are the primary components of Stevia and do not have a substantial impact on blood sugar levels. Steviol glycosides are free from carbohydrates and calories, making them a viable alternative for diabetics. Research indicates that Steviol glycosides do not influence insulin levels nor raise blood sugar.
Hence, diabetics can integrate Steviol glycosides as a sweetener into their diet to cut down on sugar intake and enhance blood sugar management. Nevertheless, it is advisable to consult a doctor or dietitian for personalized advice and adjustments.
Several factors contribute to the price differences of Stevia. Firstly, the cost depends on the form of Stevia product, be it pure Stevia powder, liquid sweetener, or sweetener tablets. Secondly, the quality of the Stevia extract significantly affects the price.
High-quality Stevia products with greater purity and concentration tend to be more costly. Additionally, supply and demand dynamics can influence the price. An increase in demand for Stevia might result in higher prices.
Stevia is often viewed as a healthier substitute for sugar due to its zero-calorie content. It can assist in reducing sugar intake and maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Compared to sugar, Stevia is significantly sweeter, so only a small quantity is required. However, the potential health effects of Stevia, particularly concerning long-term impacts or metabolic effects, remain subjects of ongoing debate and research. As with anything, both Stevia and sugar should be consumed in moderation, taking individual health needs into account.
There have been no reported instances of acute Stevia overdose. Stevia's sweetening agents, particularly Steviol glycosides, are only partially absorbed by the body and are mostly excreted unchanged. It's important to adhere to the recommended dosages and usage instructions found on the packaging or as advised by a healthcare provider or nutritionist. Since individual reactions to Stevia can vary, personal health conditions should be taken into account.
Incorporating Stevia into a healthy diet can aid in reducing sugar intake, thereby supporting weight loss efforts. Replacing sugar with Stevia can lower caloric consumption since Stevia is calorie-free and does not directly lead to weight gain. However, weight loss is influenced by various factors, and maintaining a balanced diet along with regular exercise are crucial. While Stevia can be a beneficial component, it should be seen as part of a broader healthy living strategy, not a standalone solution.
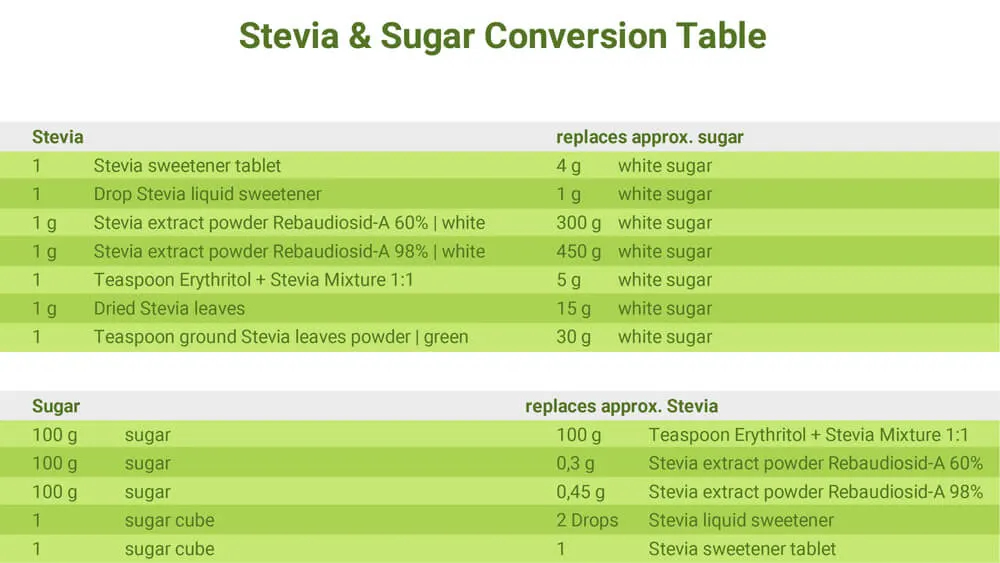
The quantity of Stevia required to substitute sugar can vary significantly based on the brand and purity of the Stevia product. Generally, 1 teaspoon of Stevia powder has approximately the same sweetening power as 1 cup of sugar. However, it is crucial to follow the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer, as the concentration and sweetness of Stevia products can differ.
Stevia products typically possess higher sweetening power and are used in much smaller quantities compared to sugar. It is advisable to begin with small amounts and adjust according to personal taste preferences.
For those aiming to lose weight, it is recommended to minimize the use of sweeteners overall. However, if an alternative is necessary, calorie-free options like Stevia, Erythritol, or sucralose can be considered.
These sweeteners have minimal or no calories and do not significantly impact blood sugar levels. Individual tolerance and possible effects on appetite should be taken into account. A successful weight loss strategy also requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and controlled calorie intake.
For weight loss, it is best to decrease total sugar intake, no matter the type. Nevertheless, some sugar alternatives may be lighter options. Coconut blossom sugar, agave syrup, or maple syrup are sometimes viewed as more 'natural' sugar substitutes. However, they still contain calories and should be consumed in moderation.
The key to successful weight loss is managing overall calorie intake and focusing on a balanced diet rich in nutrients.
The preference for Erythritol or Stevia depends on your personal requirements and taste. Erythritol is a zero-calorie sugar alcohol that closely resembles sugar in taste and texture. Conversely, Stevia is a plant-derived, calorie-free sweetener with a much stronger sweetness.
Erythritol does not impact blood sugar levels, whereas Stevia does not influence insulin levels. Your decision should be based on taste preferences, tolerance, and intended use.
No, sugar cannot be substituted directly with Stevia at a 1 to 1 ratio. Since Stevia is much sweeter than sugar, only a smaller quantity is required to match the sweetness. Generally, 1 teaspoon of Stevia powder is approximately equivalent to 1 cup of sugar. It's essential to adhere to the specific instructions provided by the Stevia product, as its concentration and sweetness may vary by brand.
Start with a smaller amount of Stevia and adjust according to your taste preferences to reach the desired sweetness.
Yes, Stevia has significantly fewer calories than sugar. While 1 teaspoon of sugar has around 16 calories, Stevia generally has no or negligible calories. It primarily consists of Steviol glycosides, which are calorie-free and not metabolized by the body.
Using Stevia instead of sugar can help lower calorie intake, which is beneficial for a calorie-restricted diet or weight loss. However, keep in mind that other ingredients in a recipe may also add to the total calorie count.
No, Erythritol and Stevia are different. Erythritol is a sugar alcohol naturally found in certain fruits and fermented foods, with about 60% of sugar's sweetening power and zero calories.
On the other hand, Stevia is a natural sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia plant, primarily composed of Steviol glycosides, which are much sweeter than sugar and calorie-free. However, Erythritol and Stevia can be combined to enhance both sweetness and texture in recipes.
Yes, Stevia can be used as a substitute for Erythritol, but it may alter the taste and texture. Erythritol has a similar feel and sweetening power to sugar, while Stevia is significantly sweeter. Consequently, Stevia is used in much smaller amounts, which can affect consistency.
It's crucial to follow recipe guidelines and make adjustments as needed to achieve the desired outcome. Combining Erythritol and Stevia can also be effective to balance sweetness and texture and is easy to measure.
There are multiple ways to substitute sugar in baking. Options include using alternatives like Erythritol, Stevia, xylitol, or coconut blossom sugar, which offer comparable sweetening power to sugar. These substitutes are often used in a 1:1 ratio to sugar, though you might need to adjust liquid content in the recipe. You can also use fruit purees such as applesauce or bananas for sweetness and moisture. Additionally, spices like cinnamon, vanilla, or cardamom can enhance flavor without adding extra sweetness. Experimenting and adjusting the sweetener amount to suit your taste is advisable.
Determining the best Stevia depends on individual preferences and needs. Many brands and products offer Stevia, so it’s crucial to look for high-quality options free from fillers and chemical additives. The form of Stevia—whether powder, liquid, or tablets—can vary based on its intended use. Customer reviews and recommendations can also guide you in finding the best product for your needs. Ultimately, trying different options will help you choose the Stevia that best meets your taste and requirements.
Yes, Stevia is free of sugar. Extracted from the leaves of the Stevia plant, it naturally contains no sugar components. Its main constituents are Steviol glycosides, which provide its sweetening power. Stevia has minimal impact on blood sugar levels and typically contains few or no calories.
It is widely used as an alternative to regular sugar by those looking to lower their sugar intake. However, always check product labels, as some Stevia products might be mixed with other sweeteners or ingredients.
No, Stevia itself naturally contains no sugar. It primarily consists of Steviol glycosides, which are calorie-free and do not impact blood sugar levels. Due to its high sweetening power, only a small quantity is required for the same sweetness as sugar.
However, some commercial Stevia products might include additional ingredients, which may contain sugar. It's crucial to read the product labels to ensure the Stevia product you select is sugar-free.
When purchasing Stevia, consider three critical factors: taste, potency, and sweetness. A premium Stevia product should have a high sweetening power with minimal aftertaste. If you previously didn't like Stevia, it might be due to the low quality of the product you tried. Many Stevia products in supermarkets contain only a small percentage of Steviol glycosides (Stevia) and are often mixed with flavors and additives like maltodextrin or sucralose. These mixtures bear little resemblance to pure "Stevia."
These two features characterize a high-quality Stevia extract:
1. Degree of purity:
A premium Stevia powder/extract should be composed of 100% pure Stevia (Steviol glycosides / Rebaudioside-A), with no fillers or additives.
2. Rebaudioside-A (Reb-A) content:
The Rebaudioside-A content should range between 60% and 98%, depending on the product. Rebaudioside-A, or "Reb-A," is the sweetest, non-bitter component of the Stevia plant.
Meeting these criteria ensures that Stevia closely mimics the taste of sugar. Many current market options, such as sticks, tabs, or crystalline powder, contain minimal amounts of Stevia. The Rebaudioside-A (Reb-A) content in these products is also typically low. But where can you find quality Stevia?
We recommend a product that fully adheres to these criteria.
Stevia is available in various forms and brands in supermarkets, health food stores, and online shops. Look for high-quality Stevia products that are free from additives. Stevia can be purchased as powder, liquid, or tablets, depending on your needs and preferences.
Before making a purchase, it is wise to compare products.
Read product descriptions to make an informed choice. Compare prices and quality to find the Stevia product that suits your needs.
The primary difference between sugar and Stevia lies in their composition and sweetness. Sugar, like white household sugar, is made of sucrose and contains calories.
Stevia, however, consists mainly of Steviol glycosides and is calorie-free. Stevia has a much greater sweetening power than sugar, requiring only a small amount to achieve the same sweetness. Stevia does not affect blood sugar levels, whereas sugar can raise blood sugar levels.
The flavor of Stevia ranges from sweet to slightly tart, depending on the quality of the Stevia product. Some people find it pleasantly similar to sugar, while others might notice a slight bitter aftertaste.
Taste perception varies among individuals. Using high-quality Stevia and the correct dosage can result in a more enjoyable taste. The form of Stevia—whether powder, liquid, or tablets—can also influence the taste. It's recommended to try different brands and forms to find your preferred taste.
Sugar substitute for diabetics
For diabetics, it is advisable to use sugar alternatives that have minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Examples include Erythritol, Stevia, and sucralose. These sweeteners have a low effect on blood sugar and can be included in a diabetic diet in moderation.
It's crucial to take into account the total carbohydrate content and individual responses to these alternatives. Consulting a doctor or dietitian is recommended to find the best options for individual diabetic needs.
Sugar alcohols like Erythritol and xylitol have minimal effects on blood sugar and feature a low glycemic index. They are absorbed and metabolized more slowly by the body. Coconut blossom sugar and maple syrup also have lower glycemic indices than regular sugar, but can still slightly elevate blood sugar levels.
Stevia, being a calorie-free sweetener, does not affect blood sugar levels as it is not metabolized. It's still vital to consider individual responses and consume these sugar alternatives in moderation.
Diabetic sugar or sugar-free sweeteners are available in numerous supermarkets, health food stores, and online shops. Search for products specifically labeled for diabetics or that offer sugar-free alternatives. Options like Erythritol, Stevia, xylitol, or sucralose may be suitable for diabetics.
Make sure to read product descriptions and ingredients to ensure they meet your requirements. Compare prices, quality, and customer reviews to find the suitable product.
Sweeteners appropriate for diabetics can be found in many supermarkets, pharmacies, and online shops. Check for products specifically labeled as suitable for diabetics or sugar-free.
Options like Erythritol, Stevia, xylitol, or sucralose can be used as sweeteners for diabetics. Carefully read product descriptions and ingredients to ensure they meet your needs. Compare prices, quality, and customer reviews to find the most suitable product.
Managing blood sugar levels is critical with diabetes. Therefore, it is best to use low-sugar or sugar-free alternatives. Sugar alcohols like Erythritol and xylitol have minimal effects on blood sugar and can replace conventional sugar.
Stevia, being a calorie-free sweetener, does not affect blood sugar levels. Coconut blossom sugar and maple syrup have lower glycemic indices than regular sugar but can still slightly elevate blood sugar and should be consumed moderately. Consult a doctor or dietitian to determine the best options for individual diabetic needs.
Several sugar substitutes have minimal effects on blood sugar levels and are suitable for diabetics. Erythritol, xylitol, and Stevia are popular options. These sweeteners are available in many supermarkets and online shops.
Carefully review product descriptions and ingredients to ensure they are suitable for diabetics. It's crucial to consider total carbohydrate content and use these substitutes in moderation. Consult a doctor or nutritionist to determine the best options for your individual needs.
Erythritol and xylitol, both sugar alcohols, are frequently used as sugar-free alternatives for diabetics. Both have minimal effects on blood sugar and provide fewer calories than traditional sugar. The primary differences lie in taste and tolerance.
Erythritol has a refreshing taste and is generally better tolerated in larger amounts. Xylitol has a mildly sweet taste but can act as a laxative if consumed in large quantities. Individual tolerance should be considered, and different options may need to be tried.
Yes, Erythritol is appropriate for diabetics. It does not significantly impact blood sugar levels or increase insulin levels. Erythritol is not metabolized by the body and has few calories, making it a suitable sugar-free sweetener to reduce sugar intake.
However, consider the total carbohydrate content and monitor individual responses to Erythritol. Consult a doctor or nutritionist to determine the best options for your specific needs.
For those with diabetes, reducing overall sugar intake is recommended. Sugar alternatives like Erythritol, xylitol, and Stevia are popular choices due to their minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
These alternatives provide fewer calories than regular sugar and can be included in a diabetic diet in moderation. It's important to be aware of the total carbohydrate content and consume them in moderation. Consulting a doctor or dietitian can help determine the best options for individual needs.
Several sugar substitutes are suitable for diabetics, such as Erythritol, xylitol, and Stevia, which have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
Selecting the best sugar substitute depends on individual preferences, tolerance, and intended use. Erythritol offers a refreshing taste and similar texture to sugar. Xylitol has a mildly sweet taste but can act as a laxative in large quantities. Stevia is a calorie-free sweetener with a high sweetening power. It's advisable to try different options and consult a doctor or nutritionist if necessary to make the best choice.